Amarans
0422 JavaScript | 문서의 기하학적 특성 | 본문
문서의 기하학적 특성
요소의 크기와 위치
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:100px;
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
</style>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
console.log(t.getBoundingClientRect());
</script>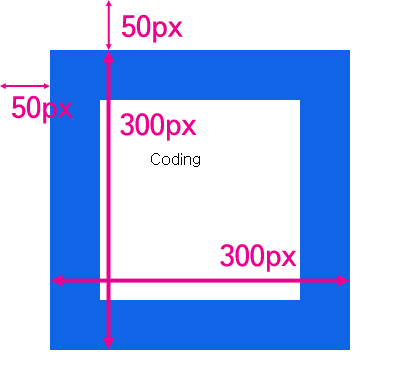
즉 엘리먼트의 테두리와 body 태그 사이의 거리가 50px이다. 그리고 테두리를 포함한 엘리먼트의 크기는 300px이다. 이 값을 알아내고 싶을 때 사용하는 API가 getBoundingClientRect이다. 이를 콘솔에서 실행한 결과는 아래와 같다.
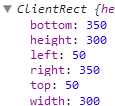
즉 엘리먼트의 크기와 위치를 알고 싶을 때는 getBoundingClientRect를 사용하면 된다는 것을 알 수 있다.
getBoundingClientRect의 width 값을 IE는 제공하지 않는다.
만약 엘리먼트가 중첩되어 있다면 어떻게 될까?
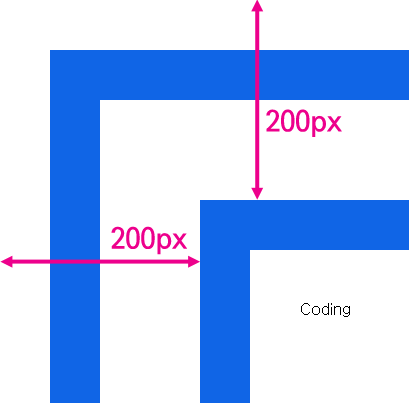
위와 같이 엘리먼트를 중첩했을 때 coding 엘리먼트와 문서와의 거리는 200px이다. getBoundingClientRect를 호출해보자.
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div{
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:100px;
}
</style>
<div>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
</div>
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
console.log(t.getBoundingClientRect());
console.log(t.offsetParent);
</script>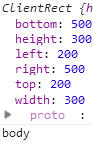
즉 엘리먼트의 위치를 의미하는 top, right의 값을 통해서 기준이 그 부모가 아니라 body라는 것을 알 수 있다. 그리고 이를 명시적으로 확인할 수 있는 방법은 offsetParent 속성을 호출하는 것이다. 만약 부모 중 CSS position의 값이 static인 td, th, table 엘리먼트가 있다면 이 엘리먼트가 offsetParent가 된다.
테두리를 제외한 엘리먼트의 크기를 알고 싶다면 ClientWidth, ClientHeight를 사용한다.
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
console.log('clientWidth:', t.clientWidth, 'clientHeight:', t.clientHeight);
</script>Viewport
viewport의 좌표
위의 그림처럼 뷰포트는 문서의 내용 중 사용자에게 보여주는 영역을 의미한다. 이에 따라서 문서의 좌표가 있고 뷰포트의 자표가 있다. 우리가 위에서 살펴본 getBoundingClientRect는 viewport의 좌표를 사용한다.
아래 예제를 실행해보면 1초에 한번씩 getBoundingClientRect의 top 속성과 window.pageYOffset의 값이 출력된다.
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div{
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:2000px;
}
</style>
<div>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
</div>
<script>
var t = document.getElementById('target');
setInterval(function(){
console.log('getBoundingClientRect : ', t.getBoundingClientRect().top, 'pageYOffset:', window.pageYOffset);
}, 1000)
</script>이를 통해서 알 수 있는 것은 getBoundingClientRect의 값이 스크롤에 따라서 달라지는 뷰포트의 좌표를 사용하고 있다는 것이다. 또한 스크롤의 정도를 알고 싶을 때는 pageYOffset을 사용하면 된다는 것도 알 수 있다.
문서의 좌표
그럼 문서의 좌표를 알고 싶으면 어떻게 해야 하나? 뷰포트의 좌표에 스크롤된 정도를 더해서 알 수 있다.
setInterval(function(){
console.log('getBoundingClientRect : ', t.getBoundingClientRect().top, 'pageYOffset:', window.pageYOffset, 'document y:', t.getBoundingClientRect().top+window.pageYOffset);
}, 1000)스크롤
그럼 문서의 스크롤 값을 변경하는 것은 어떻게 하는 것일까? scrollLeft와 scrollTop 프로퍼티를 이용하면 된다.
<style>
body{
padding:0;
margin:0;
}
div{
border:50px solid #1065e6;
padding:50px;
margin:50px;
}
#target{
width:100px;
height:2000px;
}
</style>
<input type="button" id="scrollBtn" value="scroll(0, 1000)" />
<script>
document.getElementById('scrollBtn').addEventListener('click', function(){
window.scrollTo(0, 1000);
})
</script>
<div>
<div id="target">
Coding
</div>
</div>스크린의 크기
스크린의 크기는 모니터의 크기와 브라우저 뷰포트의 크기가 있다. 이를 알아내는 방법은 아래와 같다.
<script>
console.log('window.innerWidth:', window.innerWidth, 'window.innerHeight:', window.innerHeight);
console.log('screen.width:', screen.width, 'screen.height:', screen.height);
</script>window.inner*은 뷰포트의 크기를 나타내고, screen.*은 스크린의 크기를 나타낸다.
'JavaScript2' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 0423 JavaScript | 이벤트 전파 - 버블링 / 캡처링 , 기본동작 취소 , 폼 | (0) | 2020.04.23 |
|---|---|
| 0422 JavaScript | 이벤트 | (0) | 2020.04.22 |
| 0421 JavaScript | Text객체 , 값 API , 조작 API | (0) | 2020.04.21 |
| 0420 JavaScript | jQuery 노드 변경 API , 문자열로 노드 제어 , Document 객체 | (0) | 2020.04.20 |
| 0416 JavaScript | Node 관계 , 종류 , 변경 API | (0) | 2020.04.16 |


